The diagnosis of prostatitis includes more than 5 mandatory procedures and 4 additional procedures. Just one prostate-rectal exam or ultrasound cannot tell if a man has inflammation of the prostate. The reason is that many urinary system diseases have similar clinical manifestations, and only a comprehensive differential study can eliminate the possibility of misdiagnosis.
how to pass inspection
It is recommended that men have 1-2 preventive examinations of the prostate by a urologist per year (prostatitis, adenoma and other prostate lesions are asymptomatic in the first stage). When signs of illness appear, you should see a specialist right away. These symptoms are pain in the lower abdomen and groin, difficulty urinating and getting an erection.
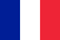
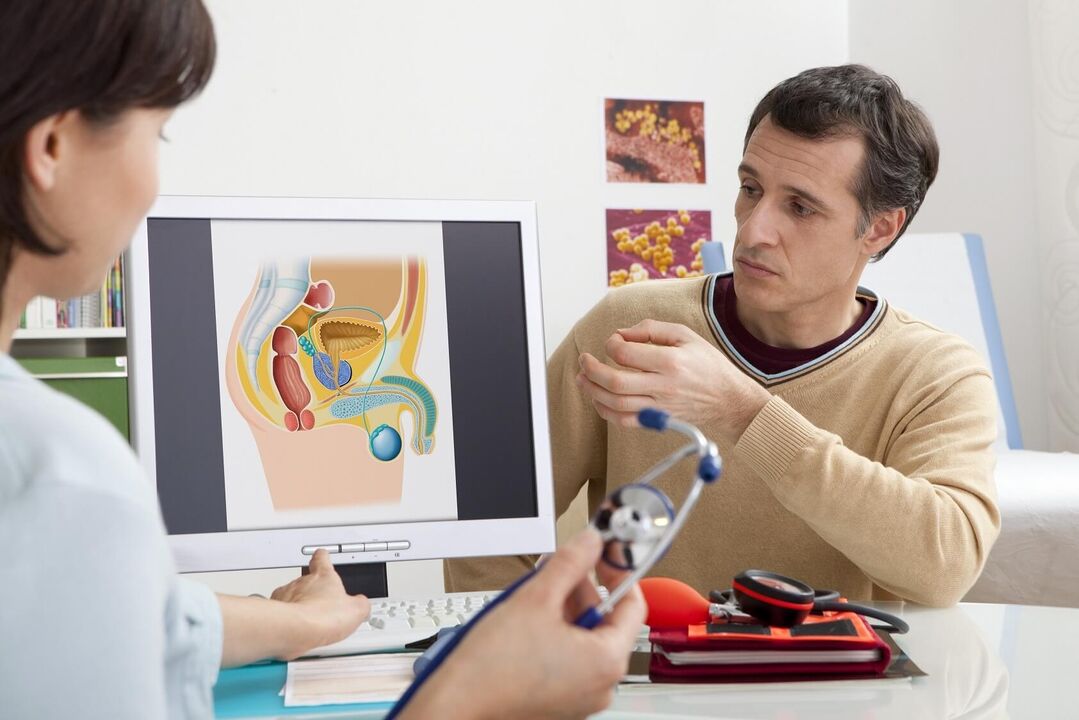
The doctor starts by collecting the patient's complaints and medical history, and then conducts a general examination. The next step in suspected prostatitis is a rectal examination (palpation of the prostate through the rectum in men). Finger studies allow physicians to assess the following parameters:
- Prostate size.
- Surface (smooth or uneven).
- Density of the gland (soft or stony).
- The presence or smoothness of the central groove.
- Men's sensitivity (whether they feel pain) when probing the prostate.
Normally, the prostate should have clearly palpable 2 symmetrical lobules with a groove in the middle. A healthy prostate is 2. 5 to 3. 5 cm in diameter and 2. 5-3 cm in length. The surface should be even, without obvious knots, and soft enough, but not loose. Any deviation from the listed features suggests prostatitis, prostatic adenoma, fibrosis, cancer, or other lesions of the genitourinary system.
analyze
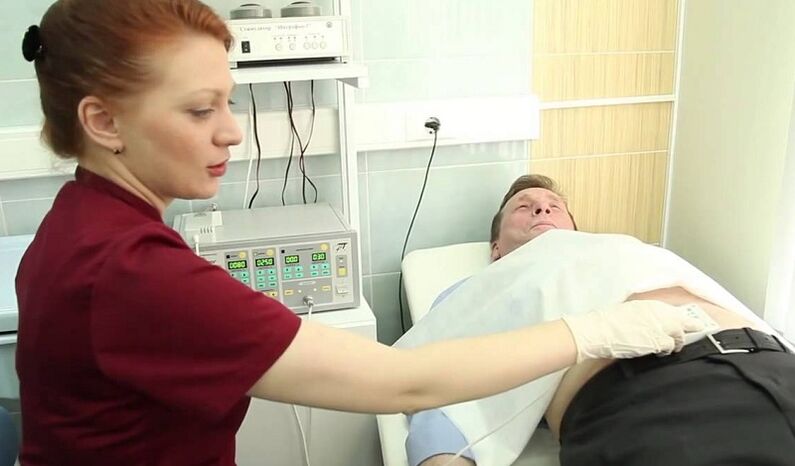
If the rectal examination and history suggest prostatitis, the urologist's next course of action is to refer the patient for laboratory testing. According to clinical standards, the following types of examinations are mandatory:
- Clinical analysis of urinalysis;
- General blood analysis;
- Seed plants with urine;
- When an infection is detected, the pathogen's susceptibility to antibiotics is determined.
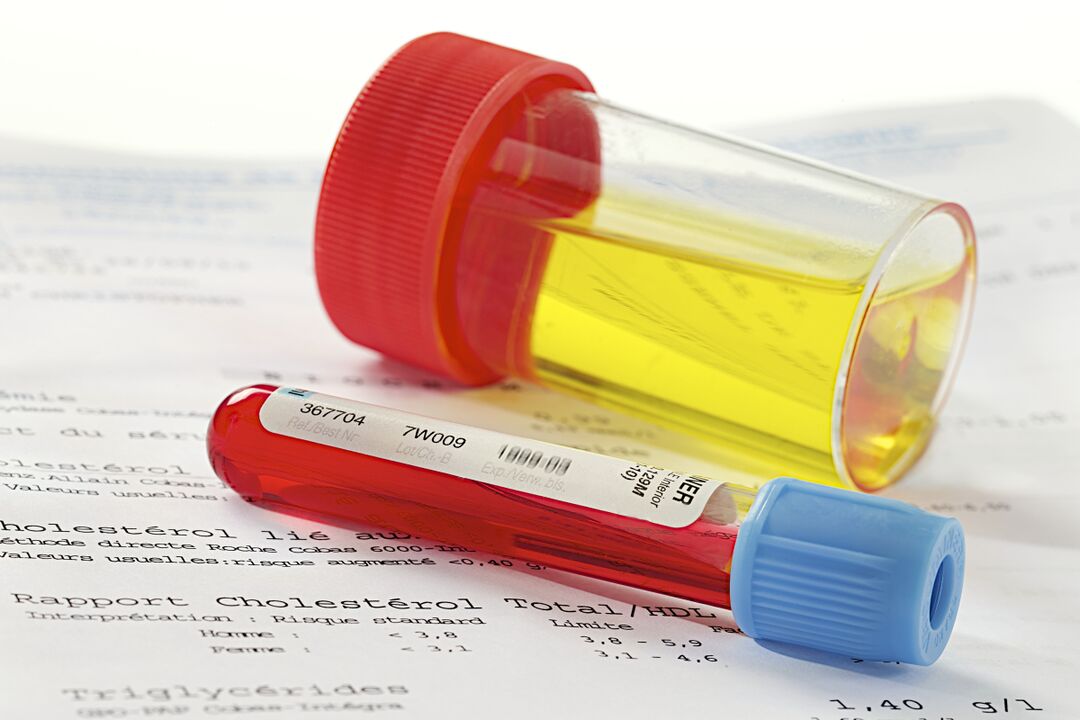
A complete blood count helps confirm acute prostatitis - with this diagnosis, the number of neutrophils increases, the white blood cell formula shifts to the left, and the level of eosinophils drops significantly. ESR can also be increased. Chronic inflammation is characterized by low hemoglobin levels (less than 100 grams per liter of blood).
To rule out prostate cancer, serum levels of PSA (a prostate-specific antigen) are measured. Its increased number indicates the presence of a tumor, but its nature (benign or malignant) cannot be determined. To find out this parameter, a biopsy of the prostate was performed and the obtained material was studied histologically.
Prostate Secrets
During a rectal exam of the prostate, the urologist will note the discharge that is secreted. Usually, it is sticky, odorless, and white. The maximum volume is 1-2 drops (3-5 mL). It should not contain pus or blood impurities, as this is a sign of disease. The consistency of the sap plays a role—if it forms clots, the man has diverticular prostatitis. A more detailed study of the material allows for laboratory studies.
Microscopic and bacteriological studies of prostate secrets are based on counts of leukocytes, lecithin granules, amyloid bodies, macrophages, pathogenic and opportunistic organisms. Prostatitis is characterized by deviations:
- Acute prostatitis: yellowish in color, slightly sweet in smell, acidic in pH, less than half of white blood cells, and 1/4 of epithelial cells.
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis: yellow or brown in color, sour smell, pH, less than half of white blood cells, macrophages (more than 15), a large number of amyloid bodies.
- Chronic non-bacterial prostatitis: the color is reddish, brown, no peculiar smell, white blood cells are normal, macrophages (10-20) can be detected, and there are many amyloid bodies.
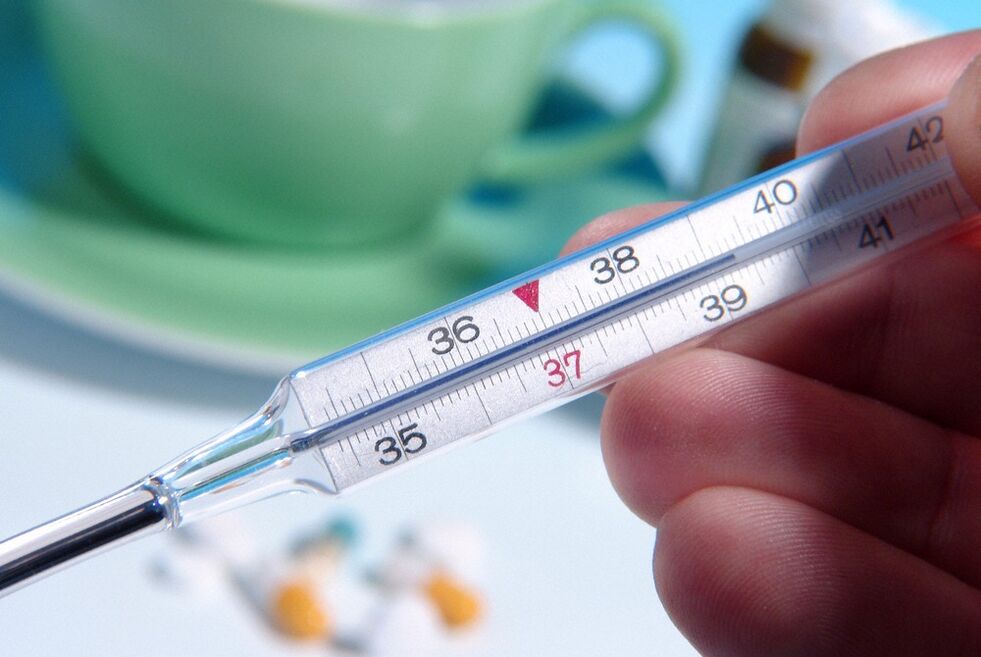
In some cases, secret studies did not allow the detection of prostatitis due to incorrect indicators. Fuzzy data would be presence of inflammation in other organs, body temperature over 39 degrees. Contraindications to rectal massage (extraction of prostatic fluid by this method) Impossibility of material sampling: exacerbation of hemorrhoids, anal fissures, tuberculosis of the prostate.
Pee
General and cytological analysis of urine requires no special preparation. Men must collect the material in containers (preferably purchased in sterile plastic containers at the pharmacy) before breakfast in the morning. A few hours before this, the patient is not advised to empty the bladder, and medication and alcoholic beverages should not be taken the day before.
In the catarrhal form of the disease, no deviation from the norm may be observed in the general analysis of the urine. With prostatitis of the last stage, suppurative threads are detected in the studied material, which precipitate.

You can diagnose leukocytosis (increased levels of white blood cells that occurs with inflammation) by studying a man's urine. A urine culture is done to determine the type of pathogen. Evidence of pathogens in the urine is associated with complications such as infectious prostatitis or inflammation of the bladder and urethra or pyelonephritis.
Urethral swab
A urethral smear is a test to confirm inflammation caused by pathogens such as Trichomonas, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Candida. Prescribe if chronic pelvic pain syndrome, itching in the groin, rash on the penis, difficulty urinating are observed. Study of collected material allows differential diagnosis - distinguishing between prostatitis, urethritis or sexually transmitted diseases, which often have similar symptoms or occur together.
Only a properly collected smear can diagnose the disease. Males must abstain from sex for 2 days before consuming this material. One hour before the surgery, do not urinate in the toilet. If the patient was taking NSAIDs or antibiotics, it would be useless to perform this analysis - the data would be incorrect.
sperm map
Spermogram - analysis of male ejaculate. In addition to prostatitis, diseases of the seminal vesicles and testicles can also be diagnosed in this way, and infertility can be detected. Submissions from men who have a temperature no higher than 39 degrees, are not taking antibiotics, and have not had intercourse for 2-3 days will be correct. Prostate massage is not recommended the day before sperm donation.
Spermograms include three types of studies. Macroscopic analysis involves studying the volume, color, viscosity, and liquefaction time of semen. Microscopic examination reveals the quantity and quality of sperm. Biochemical analysis determined the concentrations of fructose, zinc, α-glucosidase, and L-carnitine in the semen. In bacterial prostatitis, antisperm antibodies can be detected.
For prostatitis, a spermogram can reveal many abnormalities. For example, reduced semen volume (less than 1. 5 ml), low sperm concentration in 1 ml (less than 15 million), asthenozoospermia (more than 40% motile sperm), azoospermia (more than 32% motile sperm).
prostate tissue
When examining an enlarged prostate, it is not always possible to know the nature of the closure and extension with the help of a rectal examination and urine and blood tests. It can be benign pathology (adenoma, prostatitis) or malignant (cancer). An accurate diagnosis is aided by microscopic examination of prostate tissue obtained by biopsy.
The procedure is as follows: The patient inserts the ultrasonic machine sensor transrectally, at the end of which is a gun with a biopsy needle. Using a sharp tip, tiny sections of glandular tissue are excised and given to a laboratory for study. Check according to the method of comparing the material parameters with the specifications in the Gleason table.
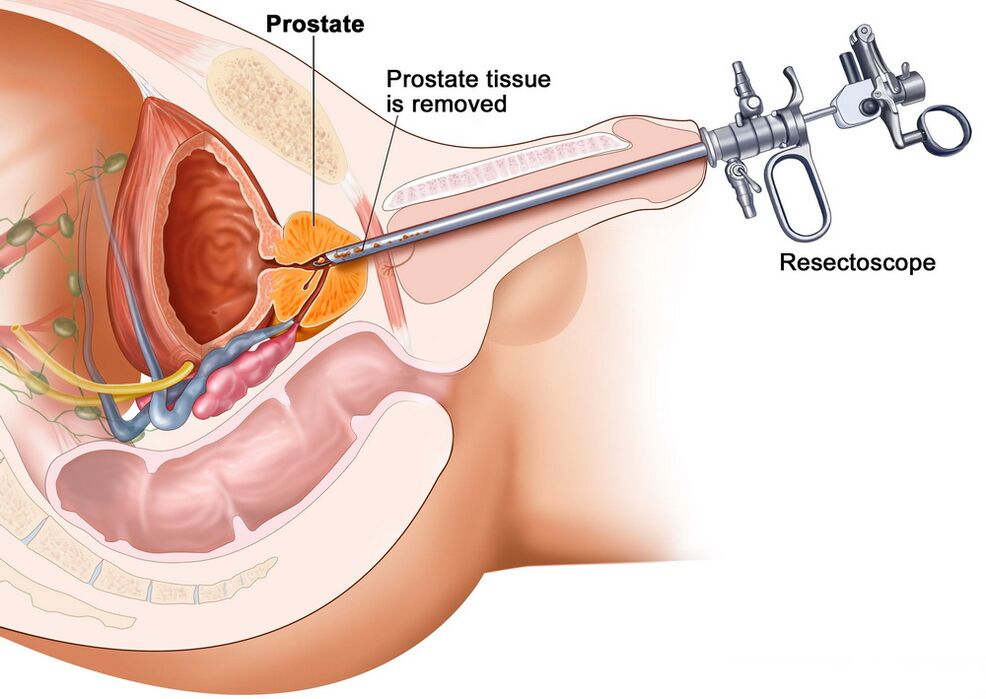
With congestive, viral, or bacterial prostatitis, the cells of the gland appear to shrink in size and the amount of connective tissue in the intercellular spaces increases. Atypical cells with altered nuclei will not be observed. If a man has prostate cancer, the cells of the gland become enlarged and clustered into clusters, and their abnormal modification becomes apparent.
Ultrasound, NMR and other methods
Instrumental studies are performed to confirm the diagnosis, as well as to determine the stage and characteristics of the disease. For lesions of the pelvic organs, the following examination methods are used:
- Traditional ultrasound;
- transrectal ultrasound;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- CT scan.
These methods allow you to understand the shape, thickness, width, length, mass, structural homogeneity, echogenicity, vascularization (vascular pattern) of the prostate gland. These parameters are required to determine urological pathology: Ultrasound, CT and MRI reveal inflammatory, proliferative and neoplastic diseases of the prostate.
Classical ultrasound has the greatest inaccuracy, but this method continues to be used because it is easy to use and affordable. Transrectal ultrasonography is considered the "gold standard" for detecting prostatitis, but it can be difficult to detect prostate cancer (especially in its early stages). MRI and CT have the highest accuracy in identifying tumors, but these are complex and expensive procedures, so they are performed when other research methods show a high likelihood of oncology.
check at home
It is possible to examine the prostate at home and identify the main symptoms of urological lesions. Of course, this would not be a diagnosis of chronic prostatitis, as the cause of the enlarged gland cannot be reliably determined. However, worrisome signs during an independent examination of a person's body are an important reason to promptly contact a urologist.
As it is, it's not worth the need to self-diagnose. Indications for home testing are:
- Impaired urodynamics (urinary frequency).
- Weak urine stream and inability to completely empty the bladder.
- Abdominal or groin discomfort (for example, painful urination).
- Decreased libido and weakened erections.
- There are purulent impurities in the urine or the color changes to white or brown.
- Nocturnal emission or seminal emission (discharge from the penis).
At home, the exam follows the same schedule as in the doctor's office. First, men need to cleanse their bowels - give an enema or take a laxative within 10-12 hours. Bathe immediately before the procedure. Then lie on your side, bend your knees, and insert your index finger into your rectum (put your fingertips in advance and apply petroleum jelly to them).
A digital rectal examination is performed by probing the back wall of the bowel and detecting the adjacent prostate. The gland is easy to spot - it feels like a small walnut to the touch. Adverse symptoms: Prostatic hypertrophy, non-round, nodules, pain on probing.These signs indicate inflammation or other pathological processes in the prostate. Once determined, be sure to see a urologist, because a more accurate diagnosis and treatment plan is needed.