Prostatitis is an inflammatory disease of the prostate. This is caused by frequent exercise in the toilet, penis pain, scrotum, rectum, sexual illness (erection, premature ejaculation, etc. ), and sometimes delays blood insurance in the urine and urine. The diagnosis of prostatitis is established by a urologist or other expert in the typical clinical chart, i. e. the results of rectal studies. In addition, ultrasound examination of the prostate, prostate secretion and urine seeding bacteria were also performed. Conservative treatment - antibacterial therapy, immunotherapy, prostate massage, lifestyle correction.
General information
Prostatitis - Seed inflammation (prostate) - Prostate. It is the most common disease in male genital system. It usually affects patients aged 25-50. According to various data, prostatitis is 30-85% of men over the age of 30. The rise in infection can cause inflammation in the upper part of the urogenital system (cystitis, pyelonephritis).
When an infectious agent is injected, the pathology develops, which enters the prostate fabric from the urogenital system (urethra, bladder) or from the remote inflammatory focus (with pneumonia, influenza, tonsillitis, pleuritis).
Causes of prostatitis
Staphylococcus aureus (Ectococci), Enterobacteria (Ectocoli), Pseudomonas (Pseudomonas), Proteus (Proteus), and klebcelllah and klebcelllah can act as infectious agents during acute processes. (Klebsiella) and E. coli (E. coli). Most microorganisms belong to conditional pathogenic bacteria, which can only lead to prostatitis if there are other inducing factors. Chronic inflammation is usually caused by Paul's association with microbial organisms.
During hypothermia, the risk of developing disease increases, and there are specific infections and conditions in the history of congestion in prostate tissues. Distinguish the following tendency factors:
- Generally, hypothermia (related to working conditions).
- A sedentary lifestyle, a person who forces a person to sit for a long time (computer operator, driver, etc. ).
- Constipation is constant.
- Ejaculation that violates the normal rhythm of sexual activity (excessive sexual behavior, long-term restraint, incomplete ejaculation in the process of depriving the emotional color of "usually" intercourse).
- The presence of chronic diseases (cholecystitis, bronchitis) or chronic infection foci (chronic osteomyelitis, ridiculous dental caries, tonsillitis, etc. ).
- Metastatic urological diseases (urethritis, cystitis, etc. ) and sexually transmitted diseases (hair disease, gonorrhea).
- Indicators that cause immune system suppression (chronic stress, irregular nutrition and inferior nutrition, frequent lack of sleep, and an overtraining state of athletes).
It is assumed that the risk of pathology increases with the increase of chronic toxicity (alcohol, nicotine, morphine). Some studies in the field of modern-day science have proven that the trigger is chronic crot bone injury (vibration, concussion) in drivers, motorcycles and cyclists. However, a large number of experts believe that all the listed conditions are not the real cause of the disease, but only leads to the intensification of the underlying inflammatory process in the prostate tissue.
The decisive role of the occurrence of prostatitis in the occurrence of prostatitis is its stagnation in the prostate tissue. Violation of capillary blood flow can lead to lipid peroxidation, edema, oozing of prostate tissue, and the development conditions of infectious processes.

Symptoms of prostatitis
Acute prostatitis
Acute prostatitis has three stages, characterized by specific clinical and morphological changes:
- Sharp Katahar. Patients complain about rapid, usually painful urination, ac bone and perineal pain.
- Sharp follicles. The pain becomes more intense and sometimes radiates to the anus, which can be exacerbated during the bowel movement. Urination is difficult and urine will flow thinly. In some cases, urine delays are noted. Fibers or moderate temperatures are typical.
- Acute parenchymal. Apparent general poisoning, high temperatures up to 38-40°C, and chills. Cervical spine disease is usually an acute delay in urination. Severe pain in the perineum. Difficult to defecate.
Chronic prostatitis
In rare cases, chronic prostatitis is the result of an acute process, however, a major chronic course is usually observed. The temperature occasionally rises to a smaller value. The patient noticed weak perineal pain, discomfort of urination and bowel movement. The most characteristic symptom is the scarcity of discharge from the urethra during bowel movements. The main chronic form of the disease develops over a long period of time. Before her, her blood stagnated in the capillaries and gradually turned into erythrocystic prostatitis.
Chronic prostatitis is usually a complication of the inflammatory process caused by a specific cause of infection (Chlamydia, urea multiple, gonococci). In many cases, symptoms of a specific inflammatory process mask the manifestation of prostate lesions. Pain during urination, weak perineum pain, and the scarcity rate of the urethra during defecation may increase slightly. Patients usually do not notice slight changes in the clinical situation.
Chronic inflammation of the prostate can be manifested through the urethra and vagina, urination, sexual disorders, and the burning sensation that increases general fatigue. The consequences of the effectiveness of the aggression (or fear of these aggressions) often become mental depression, anxiety, and irritability. The clinical situation does not always include all symptom groups of all symptoms, different patients and changes over time. Three major syndrome characteristics of chronic prostatitis: pain, violations when going to the toilet, and sexual diseases.
There is no pain receptor in the prostate fabric. The cause of chronic prostatitis pain is almost inevitable due to the abundant innervation of the pelvic organs involved in the inflammatory processes of the nerve pathway. Patients complain of pain of all magnitudes - from weak, painful to intense, sleep-violating. The nature of pain (enhanced or attenuated) with ejaculation changes as you experience excessive sexual activity or excessive sexual desire. The pain radiates to the scrotum, th bone, crot bone, and sometimes the waist area.
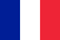
Due to the inflammation of chronic prostatitis, the volume of the prostate squeezes the urethra increases. The lumen of the ureter is reduced. The patient's urination frequently and his bladder emptying is incomplete. Usually, the phenomenon of dyslocalization is expressed in the early stages. Compensatory hypertrophy in the muscle layer of the bladder and ureters then develops. During this period, the symptoms of urination are weakening and then increasing again during the compensatory action of the adaptive mechanism.
In the initial stages, efficacy may develop, showing different manifestations in different patients. Patients may complain about frequent night erections, elimination of orgasm, or worsening of erection. Accelerated ejaculation is associated with a decrease in the level of the central excitation threshold, which is to obtain orgasm. The pain of ejaculation can lead to refusal of sexual activity. In the future, sexual disorders will become more obvious. In the advanced stage, Yangot develops.
The degree of sexual disorder depends on many factors, including the sexual constitution and the patient's psychological mood. Violation of efficacy and rehearsal can be due to two changes in the prostate and the extent to which the patient is able to inspire any inspiration. If he has chronic prostatitis, the inevitable development of sexual disorders and urination disorders is expected. Especially when it comes to the issue of functioning and toilet use, shocking patients often appear.
complication
There is a significant risk of prostate abscess without prompt treatment of acute prostatitis. When a purulent focus is formed, the patient's body temperature rises to 39-40°C, and busy characteristics can be obtained. The period of heat alternates with obvious chills. Severe pain in the perineum makes urination and makes defecation impossible.
Edema growth leads to acute delay in urination. In rare cases, an abscess can spontaneously open the urethra or rectum. When the opening enters the urethra, the abscessed urine will have an unpleasant and irritating odor, and when it is opened in the rectum, the feces contain pus and mucus.
For chronic prostatitis, a wavy route with a prolonged remission cycle is characteristic, during which inflammation of the prostate can cause potential or show extremely meagre symptoms. Patients without any distress often discontinue treatment and only translates as complications develop.
The most common complications of chronic processes are inflammation of the testicles and inflammation of the appendages of the testicles and the seed bubbles. The consequence of these diseases often becomes infertility.
diagnosis
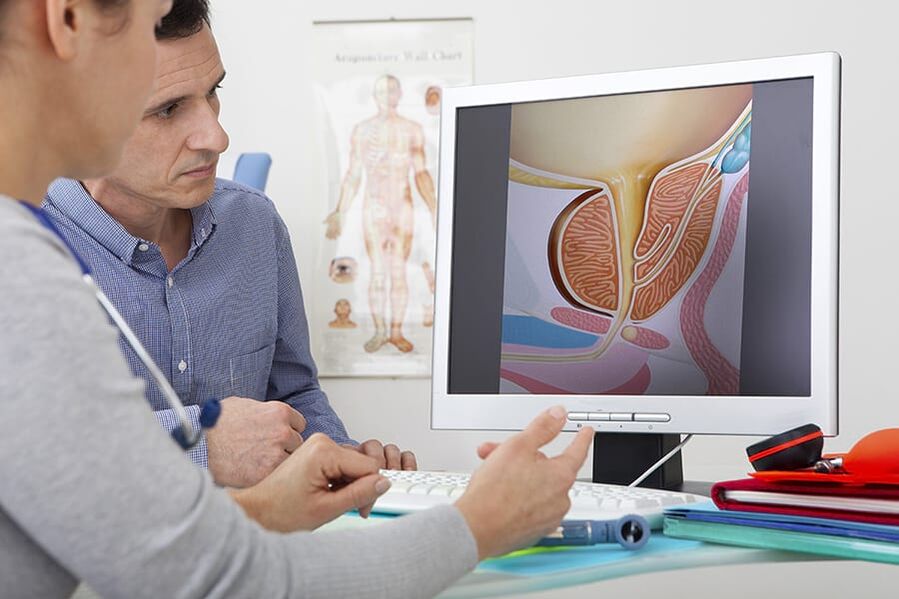
A characteristic clinical condition simplifies the diagnostic process of acute and chronic prostatitis. Enforcement:
- Rectal study of the prostate
- The fence secreted by the prostate determines the sensitivity of the bacterial population (the secret of sowing the prostate and sowing urine to the bacteria).
- Ultrasound examination of the prostate to identify structural changes (tumours, cysts, adenomas) and the differentiation of prostatitis from other diseases
- Sperm map excludes or confirms the development of infertility.
Treatment of prostatitis
Treatment of acute prostatitis
Patients without complications undergo treatment in the outpatient clinic by the urologist. Through severe poisoning, suspicion of the suppurative process was pointed out in hospitalization. Perform antibacterial treatment. These drugs were selected considering the sensitivity of the infectious agents. Antibiotics are widely used and can penetrate well into prostate tissues (ciprofloxacin, etc. ).
As acute urination delay develops, in the context of prostatitis, they can install special tubes instead of urethral catheters because there is a risk of prostate abscess. As the abscess develops, an extra-endoscopic rectal or urethral opening of the abscess is performed.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
The treatment of chronic prostatitis should be complex, including courses of treatment, physical therapy, and immune correction:
- Antibiotic therapy. The patient was prescribed for a long-term antibacterial course (within 4-8 weeks). Determination of the type and dosage of antibacterial drugs and duration of treatment was performed separately. The drug is selected based on the sensitivity of the bacterial flora based on urine seeds and the results of prostate secrets.
- Prostate massage. Massage of the glands has a comprehensive impact on the affected organs. During massage, inflammation accumulated in the prostate is secretly squeezed into the duct and then entered the urethra and removed from the body. This process improves blood circulation in the prostate, thus minimizing stagnation and providing optimal antibacterial penetration into tissues of affected organs.
- physiotherapy. To improve blood circulation, laser exposure, ultrasonic waves and electromagnetic vibration are used. If it is impossible to perform a physical therapy procedure, prescribe the patient to a warm small medical level.
In chronic, long-term inflammation, immunologists are consulted on strategies for immunocalibration therapy. Provides patients with lifestyle changes. Some changes in lifestyle changes in patients with chronic prostatitis are both therapeutic and preventive measures. It is recommended to normalize the patient's sleep and awakening to establish a diet and perform moderate physical exercise.

Predict and prevent
Acute prostatitis is a clear trend in a chronic trend. Even if timely and appropriate treatment is available, more than half of the patients will have chronic prostatitis. However, by treating in the right order and following the doctor’s advice, recovery is far from often possible, eliminating unpleasant symptoms and prolonging remission during chronic processes.
Prevention lies in eliminating risk factors. It is necessary to avoid hypothermia, replace sedentary work and physical exercise periods, and eat regularly. Use constipation, laxatives should be used. One of the preventive measures is the normalization of sexual life, as excessive sexual activity and sexual abstinence are risk factors for the development of prostatitis. If symptoms of urology or sexually transmitted diseases occur, you need to consult a doctor in time.